In the world of digital landscapes, where control over our files and folders is essential, few things are as frustrating as encountering the message, “You Require Permission from Administrators to Make Changes to this Folder.” It’s like hitting a roadblock when you’re in a hurry, but fear not, for in this article, we’re going to unravel the mysteries behind this message. We’ll equip you with the knowledge and tools to understand, address, and conquer this all-too-common obstacle in the realm of Windows permissions. Whether you’re a seasoned tech enthusiast or a newcomer to the world of computing, by the end of this journey, you’ll be confidently making changes to your folders, hassle-free.
Check also: Best Ge Dishwasher
Table of Contents
Fix You Need Permission From Administrators To Make Changes To This Folder
If you’re seeing the message “You Require Permission from Administrators to Make Changes to this Folder” in Windows, it means that your user account does not have the necessary permissions to make changes to the folder in question. To fix this issue, you can try the following steps:
METHOD I: Boot into Safe Mode
Safe Mode is a special diagnostic mode in Windows that loads a minimal set of drivers and services, designed to help users troubleshoot and fix various issues, including problems related to software, drivers, or system settings. When your computer is in Safe Mode, it runs with a limited set of features to help identify and resolve issues that might not be apparent in normal operation. This mode can be incredibly useful when trying to diagnose and fix problems, such as those related to permissions, malfunctioning drivers, or malware infections.
Open the Windows Start Menu or Desktop:
You can initiate the process from either the Windows Start Menu or the Desktop, depending on your preference.
Hold Down the Shift Key:
On your keyboard, locate the “Shift” key. Press and hold it.
Access the Restart Option:
- While holding the “Shift” key, locate the “Restart” option. You can access this option in one of two ways:
- If you are using the Windows Start Menu, click the “Start” button, and then, while holding “Shift,” click the “Power” option. This will reveal the “Restart” option.
- If you are on the Desktop, you can press and hold the “Shift” key while clicking the “Restart” option from the Power menu. You can typically find the Power menu by clicking on the Windows icon in the lower-left corner of your screen or by pressing “Ctrl + Alt + Delete” and selecting “Power.”
The Blue Screen with Options:
Upon selecting “Restart” while holding down the “Shift” key, your computer will immediately initiate the restart process. Instead of the standard reboot sequence, your computer will show a blue screen with advanced options.
Choose “Troubleshoot”:
On the blue screen with options, you will see several choices. Among them, select “Troubleshoot.”
Access “Advanced Options”:
Within the “Troubleshoot” menu, you’ll find various advanced options for diagnosing and repairing your system. Click on “Advanced options.”
Select “Startup Settings”:
Inside the “Advanced options” menu, you will find various tools and settings for advanced troubleshooting. Locate and click on “Startup Settings.”
Initiate Another Restart:
After selecting “Startup Settings,” you’ll be presented with a screen that details what this option does. To proceed, click the “Restart” button.
Startup Settings Menu:
Following the second restart, your computer will restart again and display a menu known as “Startup Settings.” This menu provides a list of different startup options.
Choose Your Safe Mode Option:
The Startup Settings menu typically lists various options, including different Safe Mode configurations. To boot into Safe Mode, you’ll need to select one of the corresponding number keys. The typical options include:
“Safe Mode” (usually assigned to the key “4”) for standard Safe Mode.
“Safe Mode with Networking” (usually assigned to the key “5”) for Safe Mode with networking support.
Final Restart:
Once you’ve made your selection by pressing the corresponding number key, your computer will initiate another restart. This time, it will boot into the chosen Safe Mode configuration.
In Safe Mode:
After successfully completing the steps above, your computer should boot into the selected Safe Mode. In Safe Mode, you’ll notice that the desktop may look different, and many features and drivers will be limited to facilitate troubleshooting.
Using Safe Mode: Safe Mode is used for various troubleshooting tasks, including fixing issues with permissions, resolving driver conflicts, removing malware, or addressing issues that prevent your computer from starting normally. In Safe Mode, only essential system drivers and services are loaded, which can help you pinpoint and resolve problems.
Exiting Safe Mode: To return to normal mode from Safe Mode, you can simply restart your computer. After restarting, it will boot back into the standard operating mode.
METHOD II: Use Command Prompt
One of the most common and sometimes frustrating scenarios in Windows is when you come across the message “You Require Permission from Administrators to Make Changes to this Folder.” This roadblock can occur when you need to make essential changes to files and folders on your system. Fortunately, there’s a powerful tool at your disposal – the Command Prompt. In this article, we will walk you through a detailed and advanced method using the Command Prompt to take ownership of a folder and modify permissions. By the end of this guide, you’ll have the knowledge and confidence to resolve these permission issues and regain control over your files.
Step 1: Open Command Prompt with Administrator Privileges
- To begin, press the
Windows + Skeys to open the Windows Search bar. - Type “cmd” or “Command Prompt” into the search bar.
- Right-click on “Command Prompt” or “cmd” in the search results.
- Select “Run as administrator” from the context menu. This will launch Command Prompt with administrative privileges, which are necessary for making system-level changes.
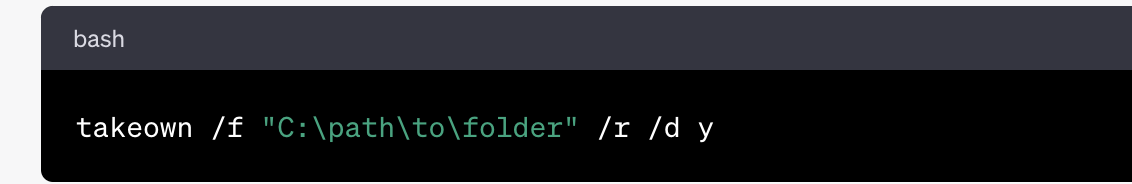
Step 2: Use the takeown Command
- In the Command Prompt window, you’ll first need to use the
takeowncommand to take ownership of the folder that is giving you permission issues. Thetakeowncommand is used to take ownership of files and directories on your system. - To take ownership of a folder, use the following command format:
Replace "C:\path\to\folder" with the actual path to the folder you want to take ownership of. The /r flag is used to apply the command recursively to all subfolders and files within the specified folder and /d y is used to confirm that you want to take ownership.
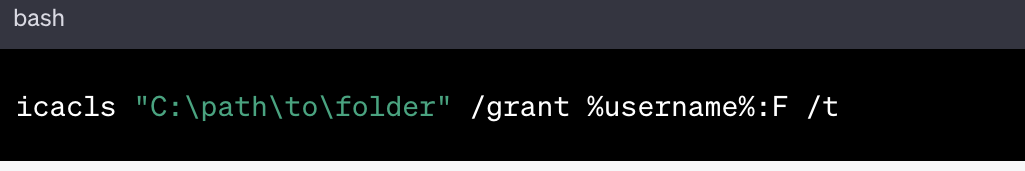
Step 3: Use the icacls Command to Modify Permissions
- After taking ownership of the folder, you can use the
icaclscommand to modify the permissions on the folder and its contents. Theicaclscommand is powerful and allows you to control access and permissions for files and folders. - To modify the permissions of the folder, use a command like the following:
"C:\path\to\folder"should be replaced with the actual path to the folder you’re working with.%username%is a variable that represents your user account. This command grants full control (F) to your user account.
The /t flag is used to apply the permissions recursively to all subfolders and files.
Step 4: Confirm and Test Changes
- Once you’ve executed the
icaclscommand, it will apply the specified permissions to the folder and its contents. You should see a confirmation message in the Command Prompt. - To verify that the changes have taken effect, navigate to the folder in File Explorer and attempt to make the changes or modifications you initially intended. You should no longer encounter the “You Require Permission from Administrators” error.
The Command Prompt is a powerful tool for taking ownership of folders and modifying permissions when Windows restricts your access. By following these steps, you can confidently resolve permission issues and regain control over your files and folders. It’s important to use this method with caution and ensure that you understand the implications of modifying permissions, as incorrect changes can affect the stability and security of your system.
FAQs
1. What does the message “You Require Permission from Administrators to Make Changes to this Folder” mean?
This message indicates that your user account lacks the necessary permissions to modify a specific folder or its contents. It typically occurs when you attempt to access, delete, or modify files or folders in Windows, and the operating system restricts your actions due to security settings.
2. Why do I encounter this message in Windows?
- There are several reasons why you might encounter this message. The most common causes include:
- Insufficient permissions for your user account.
- The folder is protected by the system or another user.
- Ownership of the folder is not assigned to your account.
- Security settings, such as access control lists (ACLs), are restricting your access.
3. How can I resolve this issue?
- There are multiple methods to address this issue, including:
- Taking ownership of the folder.
- Modifying permissions through the Properties window.
- Use the Command Prompt to take control and adjust permissions.
- Running programs or performing actions as an administrator.
- Disabling User Account Control (UAC), although this is not recommended for security reasons.
4. Is it safe to use the Command Prompt method to resolve this issue?
Using the Command Prompt method to modify folder permissions can be safe and effective when performed correctly. However, it’s essential to exercise caution and have a good understanding of what you’re doing, as improper usage can lead to unintended consequences. Always back up important data before making changes.
5. What are folder permissions, and how do they work?
Folder permissions control who can access, read, write, or modify files and folders in Windows. Permissions are assigned to user accounts or groups and are defined by access control lists (ACLs). These permissions determine the level of access and control each user has over the folder’s contents.
6. Can I resolve this issue if I’m not the administrator of the computer?
If you are not the administrator of the computer, you may still be able to resolve this issue by requesting assistance from the system administrator. Alternatively, you can try some of the methods mentioned in the previous responses, such as taking ownership, but it depends on your level of access and the specific security policies in place.
7. Are there any risks involved in taking ownership of a folder?
- Taking ownership of a folder should be done carefully, as it can impact system security and stability. If you take ownership and modify permissions incorrectly, it might affect system files or open up security vulnerabilities. Always proceed with caution and ensure you understand the consequences of your actions.
8. What other messages or errors can I encounter related to folder permissions?
- In addition to the “You Require Permission from Administrators” message, you might encounter various other errors, such as “Access Denied,” “File/Folder is in Use,” or “You Do Not Have Permission.” These messages are typically related to permission issues and may require similar troubleshooting steps.
9. When should I contact IT support or a professional for help with folder permission issues?
- It’s a good idea to contact IT support or a professional when you are uncertain about how to proceed, especially if you are dealing with sensitive data, critical system files, or networked environments. They can provide expert guidance and help ensure that your actions align with organizational policies and best practices.
10. Can I permanently disable folder permissions in Windows?
- It is not recommended to permanently disable folder permissions in Windows, as they play a crucial role in maintaining system security and access control. These permissions are in place to protect your system and data from unauthorized access and modifications. Disabling them could expose your system to security risks.

Virat Raj is a Digital Marketing Practitioner & International Keynote Speaker currently living a digital nomad lifestyle. During his more than 10 years-long expertise in digital marketing, Virat Raj has been a marketing consultant, trainer, speaker, and author of “Learn Everyday yourself: In Pursuit of Learning” which has sold over 10,000 copies, worldwide.